Synapse Dataops
Implement Synapse CI / CD for Data Lakes
In this post we will cover an end to end synapse CI / CD implemenation for Data Lakes for enterprise deployments. This blog takes inspiration from the Modern Data Warehouse which is based on the github repository.
For this blog we focus on using Azure DevOps as our Workspace Repository.
Pre-requisites:
- Azure Synapse Workspace
- Azure DevOps Project
- An IDE of your choice , for this blog i have used VS Code
- Synapse Workspace Deployment extension on your azure devops project.
- SQL Server Extension For VS Code
- Service Connection with contributor rights on the resource group and Synapse Administrator rights on the Workspace on higher envs.
Scenario :
Steps in this project :
- Link Synapse Workspace Created to a Azure DevOps Repository
- Developers Create a new branch to work on , this is done on the sandbox environment
- Developers Create Features
- Developers Create Tests
- Raise Pull Request to merge into the release branch
- Build Pipleine needs to be created which creates build artifacts for release step
- Release Branch is Deployed into the Dev Environment using Azure DevOps Pipelines
- Frozen Artifacts are deployed into Acceptance and Later production after integation tests have passed
Steps Elaborated :
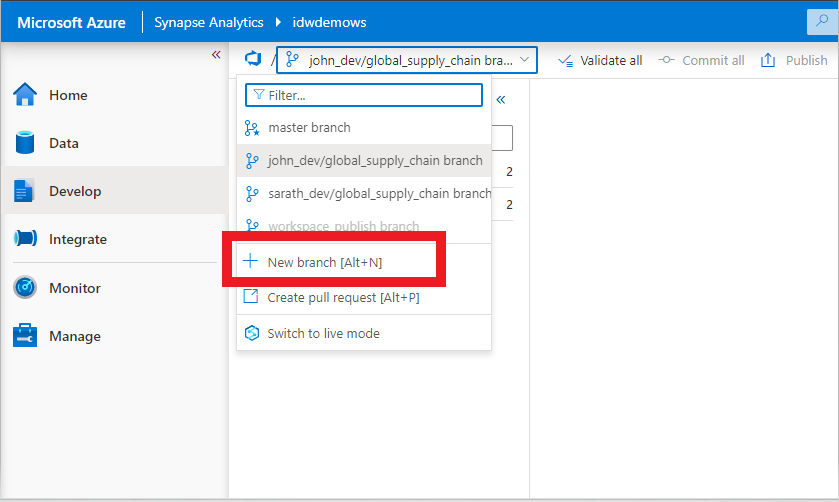
2. Developers Create Branch
Let us take the example of a sprint developement. As a developer A we create a new branch of our Synapse Workspace to start working on a feature which needs to be developed in this sprint.
First step is to create a new branch , this can be done from synapse workspace in the sandbox environment. Point to note , on the sandbox environment there is one synapse workspace deployed , where developers have Synapse Administrator Access.
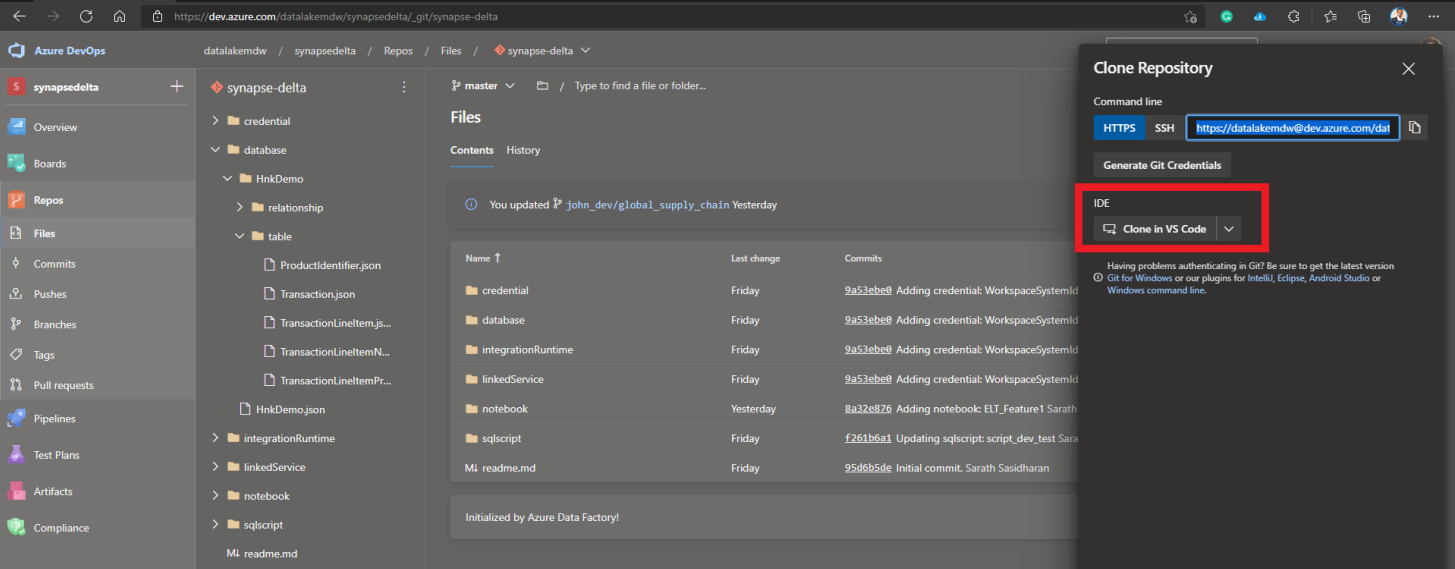
Once the branch has been created , the developer clones the project into his/her IDE of choice , in this case we use VS Code. Azure DevOps has a feature to directly clone this project into VSCode. Git Clone , could also be used to get this project locally into your IDE.
3.Developers Create Features
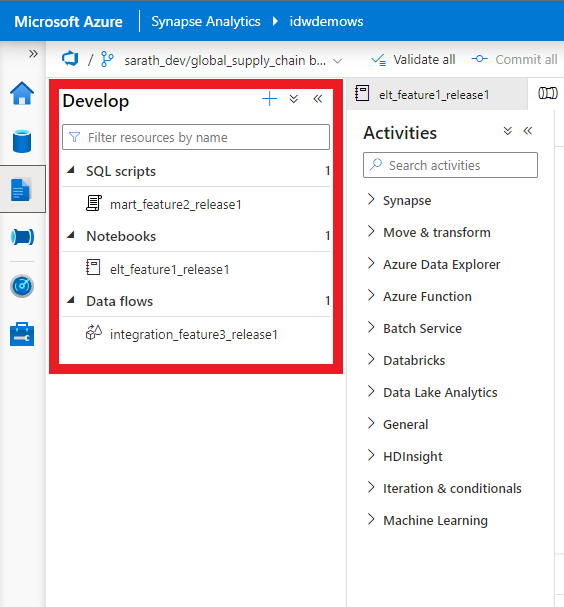
After the branch is checked out for developement , the next step is for the developer to start working on the feature assinged in the current sprint.
Taking an example of 3 artifacts being developed in this sprint , feature1 and feature2,feature3. Let’s assume that feature1 is a functionality in spark , which is written inside a spark notebook and the second feature is a SQL Script which creates a new table and a stored procedure and feature3 consists of a mapping dataflow. In this situation we would like to check in 3 features which are all different scopes , into this single release.
For this release , developer 1 has created 3 features for Release 1.0 . They are namely:
- Spark notebook to perform an ELT and create a spark table
- A SQL Script to create a new table and populate the data into the data mart
- A Data Flow to copy the data from staging area into the data mart and the corresponding trigger
These generate 4 artifacts in our workspace, namely a spark notebook , a sql script , dataflow and a trigger file.
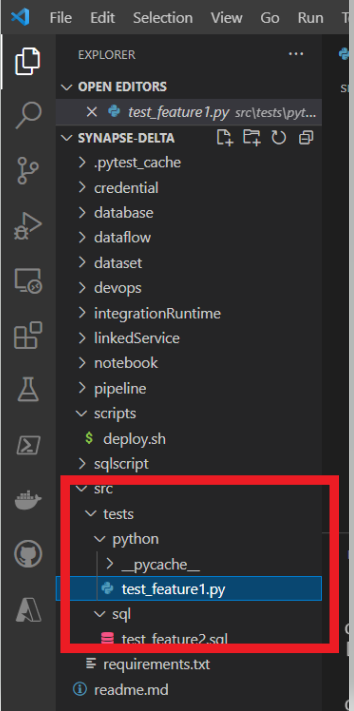
4.Developers Create Tests
After the feature have been created the next step is to create unit tests for these features. We have 3 features :
- Pyspark script for extraction of raw to clean data
- Data Flow to get the data into a Kimball model
- SQL objects
For testing , pyspark scripts we can use the pytest package and run asserts on the logic / functions. For SQL Objects the idea would be to leverage tsql-t and sql server unit tests
5.Developers Create a Pull Request to Merge to main Branch
Once the tests have been defined developers would like to push these 3 features into the main branch. In order to maintain sanity on the main branch , the need to have a pull request validation pipeline is essential.
In order to to do this , a PR validation pipeline needs to be created in Azure DevOps.
Note : Variable used in these scripts are set as variables within Azure DevOps within a Variable Group , these values are stored inside Azure KeyVault for security purposes.
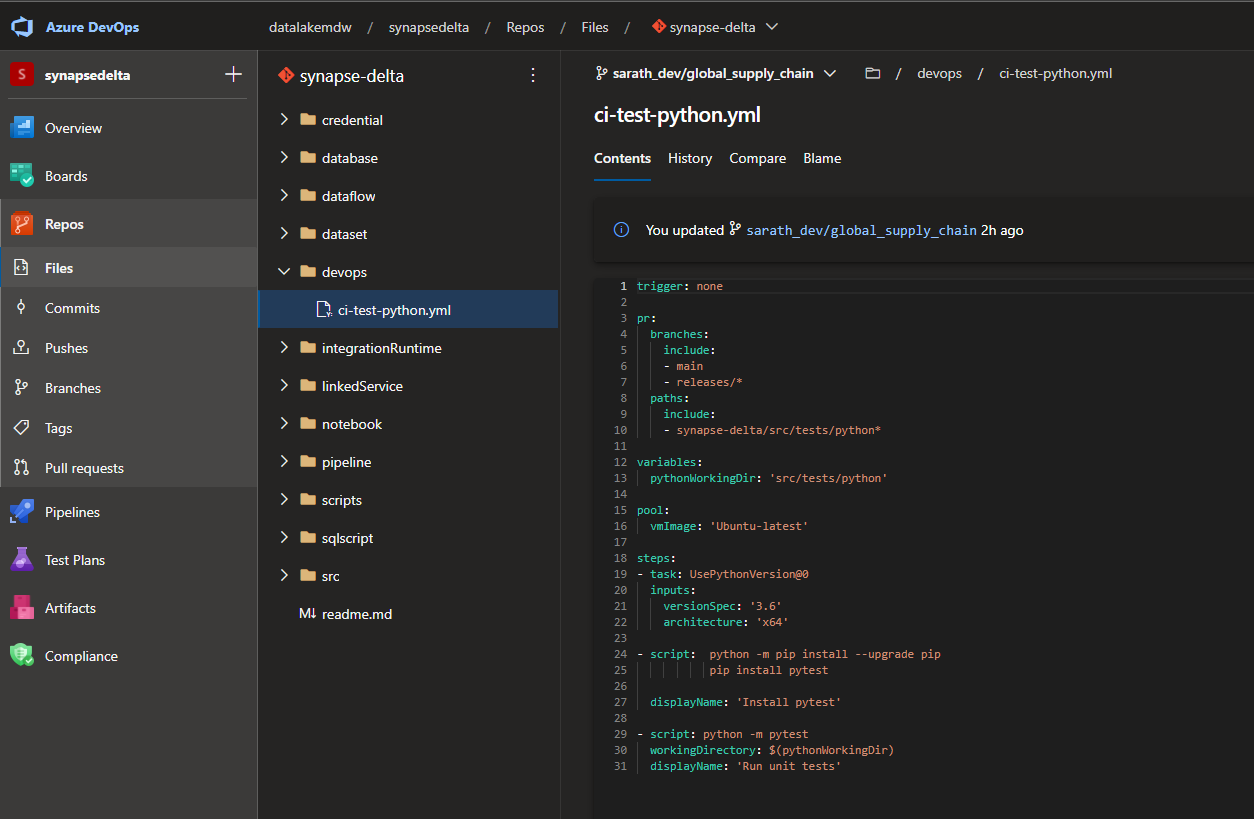
The basic pipeline script for PR Validation for the python script :
trigger: none
pr:
branches:
include:
- main
- releases/*
paths:
include:
- synapse-delta/src/tests/python*
variables:
pythonWorkingDir: 'src/tests/python'
pool:
vmImage: 'Ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '3.6'
architecture: 'x64'
- script: python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install pytest
displayName: 'Install pytest'
- script: python -m pytest
workingDirectory: $(pythonWorkingDir)
displayName: 'Run unit tests'
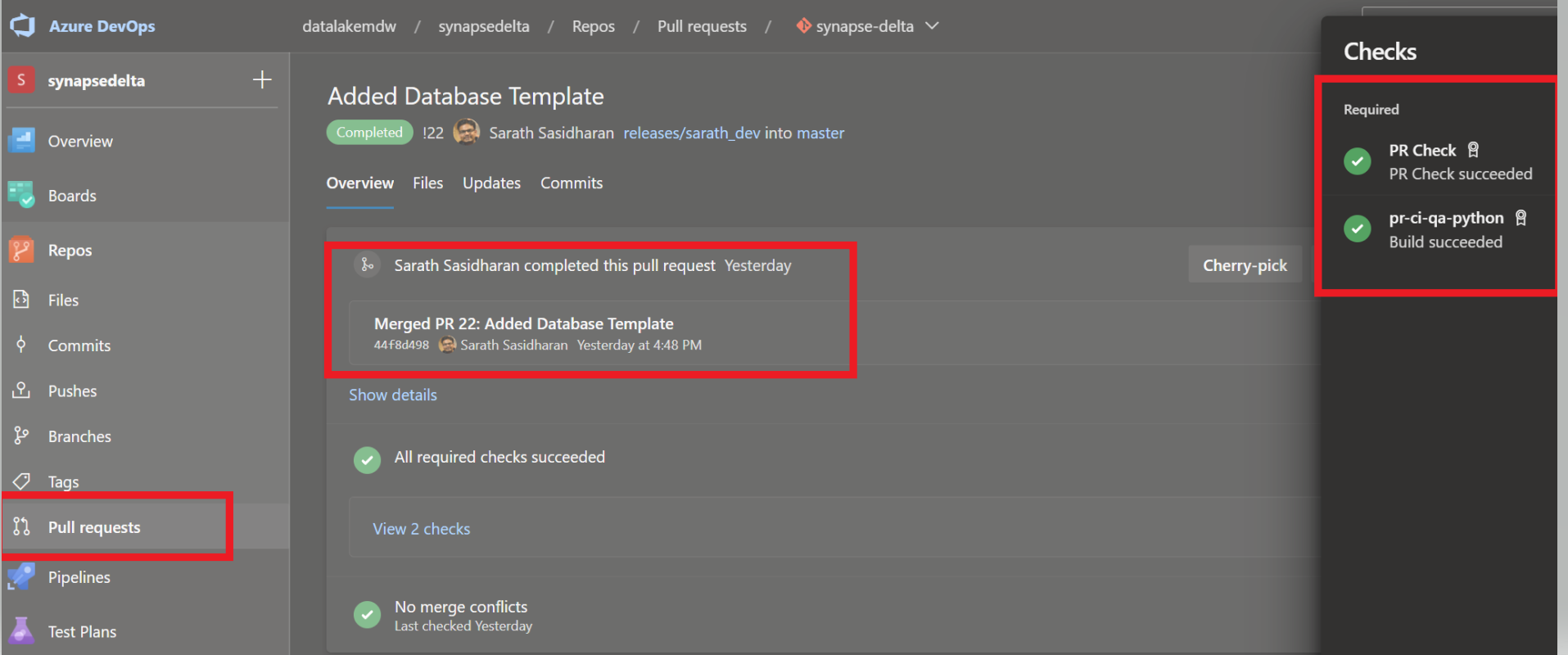
This pipeline uses a Pull Request trigger , which would mean every PR raised by the dev team , triggers this PR validation script which runs the Unit tests. If this test succeeds then a merge to main branch is done.
Only if the tests and the build are succesful then the merge to main branch is made possible.
A validation check is placed on the merge to main branch , which always depends on the success of the PR pipeline.
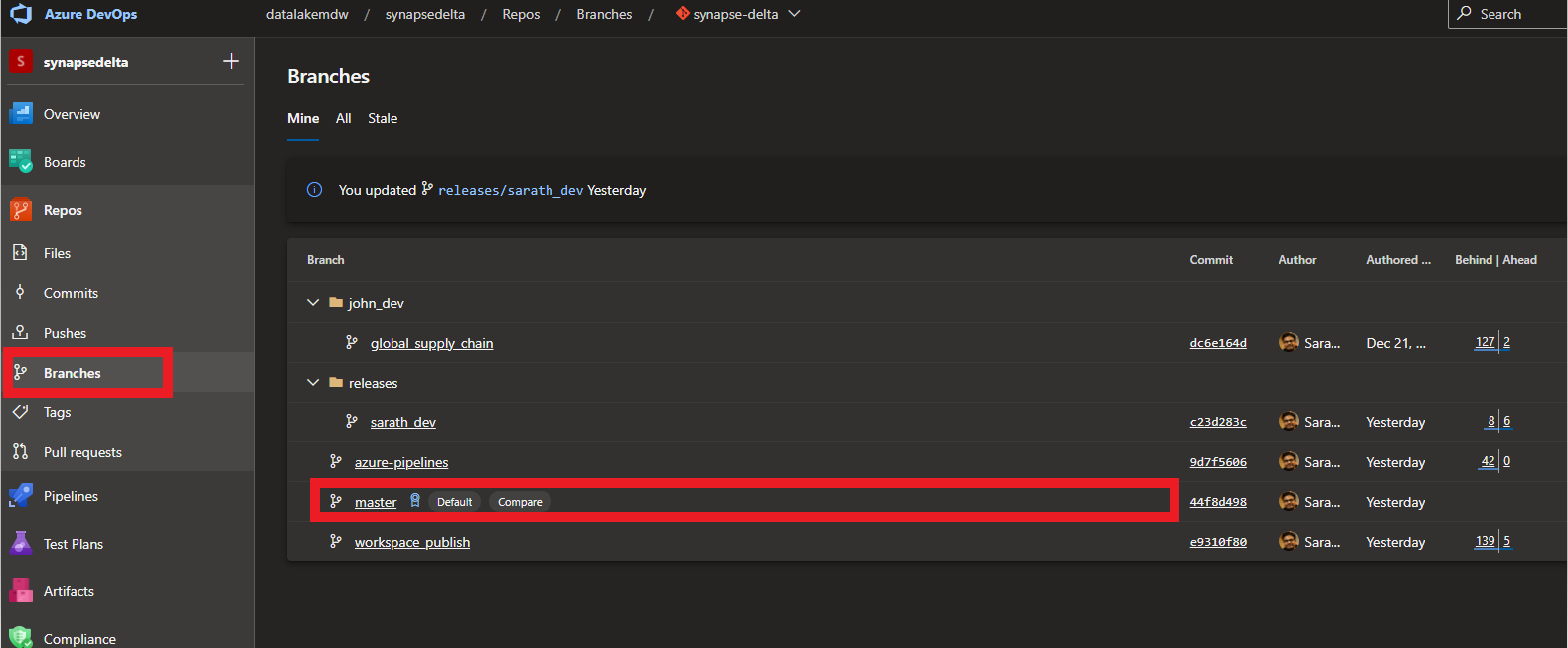
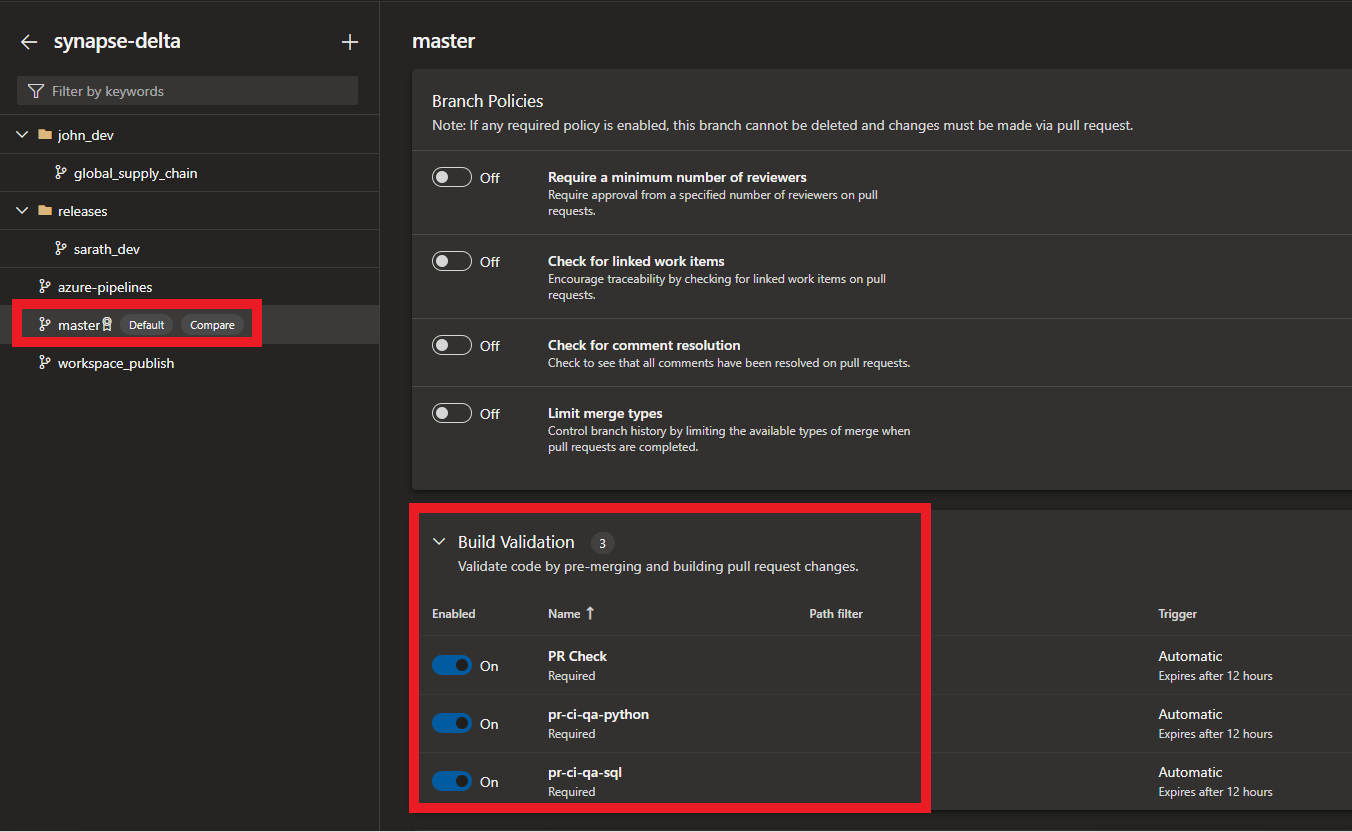
This is done by setting the branch policy in Azure DevOps on the main Branch. This can be found under the Repos section.
Select the branch which needs to be checked before merge ( in this case master) and under the build validation , add the pipelines which needs to pass before the merge is succesful. This check prevents failed builds from landing on the main branch.
Once this is setup , the next step is to raise the PR. 3 Features which the developers have build are ready to be shipped to the main branch. In order to do this , the developers create a PR to merge thier changes onto the main branch.
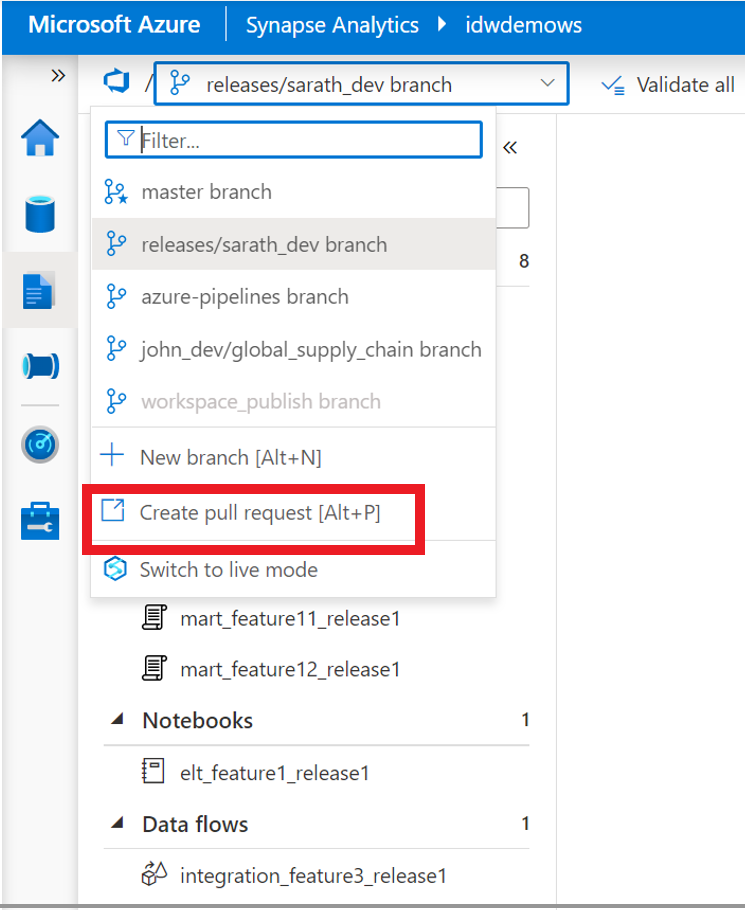
For this example lets take of example of developer 1 , who has created 8 features for sql pools , 1 for elt (spark notebook) , 1 data flow and a trigger file.Once the local /sandbox tests are complete the developer is ready for pushing this to the master branch for the dev release.In order to do this , in this example the Pull request is raised from the Synapse Workspace UI which the developer has linked to his branch.
6.Pull Request is merged into the release branch
Once the pull request has been raised the PR pipelines are triggered automatically .
Pipeline for PR sql build script
trigger: none
pr:
branches:
include:
- main
- releases/*
paths:
exclude:
- README.md
variables:
sqlDwPath: 'synapse/synapsepools'
sqlDwSolutionName: 'synapsepools'
sqlDwSolution: '$(sqlDwPath)/$(sqlDwSolutionName).sqlproj'
buildPlatform: 'Any CPU'
buildConfiguration: 'Debug'
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
steps:
- task: NuGetToolInstaller@1
- task: NuGetCommand@2
inputs:
restoreSolution: '$(sqlDwSolution)'
- task: VSBuild@1
inputs:
solution: '$(sqlDwSolution)'
platform: '$(buildPlatform)'
configuration: '$(buildConfiguration)'
For github this leverages the PR trigger which has been added inside the yml file . For azure devops though , you have to do it via the step described earlier (branches-> branch policy)
This would trigger the PR pipleines which have been configured to run the unit tests and create the build (for sql). The merge request would only succeed if the PR pipelines have run succesfully.
7.Build Pipelines for Generation of Build Artifacts
After the PR validation is done and the scripts have been merged into the main branch . Next step is to bundle the artifacts for deployment. This process is split up into 2:
- Build artifacts for SQL , which include , dacpac build for SQL Dedicated Pools and Python packages / scripts and libraries to be installed
- Build artifacts for Workspace , which are , notebooks , sql scripts (SQL Serverless + SQL Scripts) , Data Flows , Triggers , Linked Services , Datasets etc.
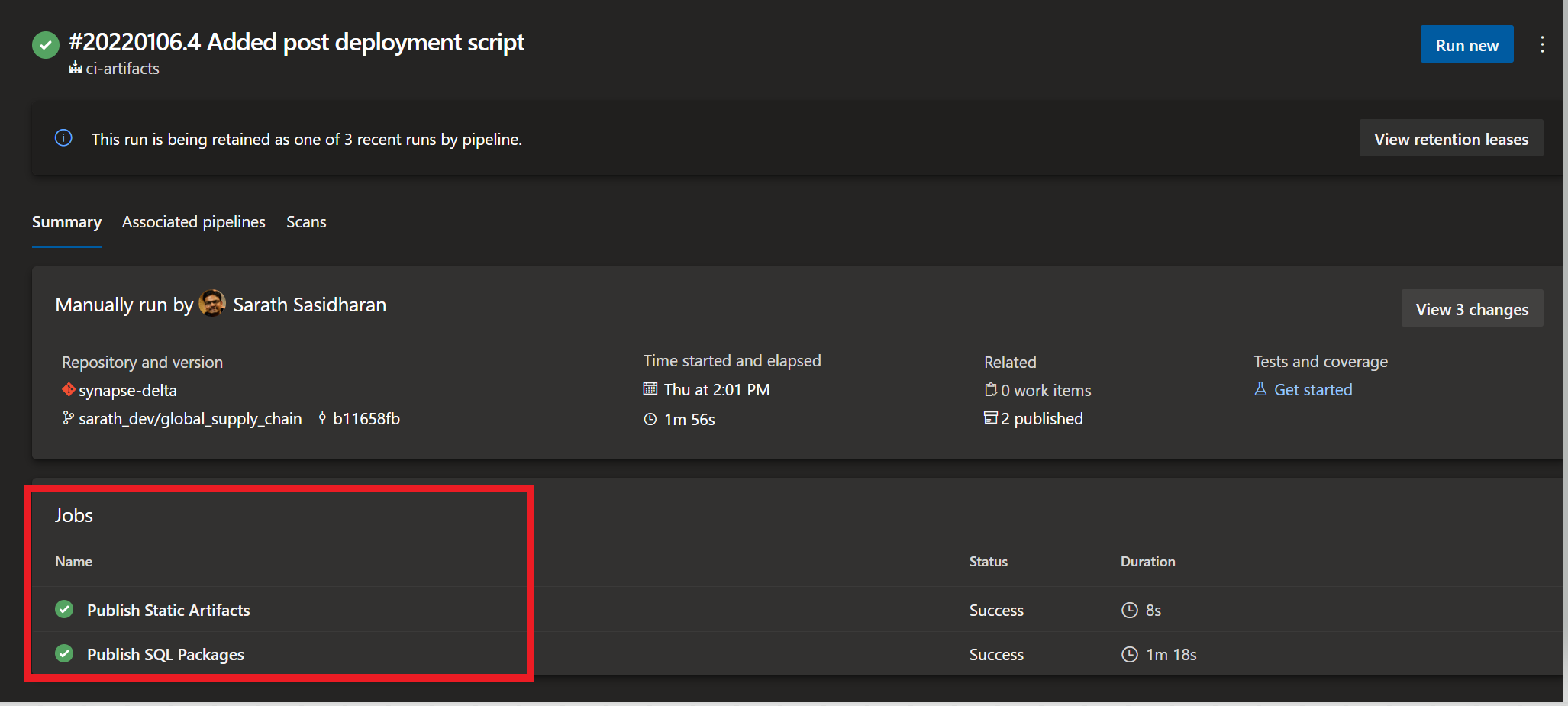
For step 2 , there is a manual process involved , which would require us to publish the changes from the main branch. This generates the workspace template and also the parameter template which is automatically written into the workspace_publish branch. This will be automated in the future , where you could use a npm package to check this out automatically , rather than having to manually publish this.
The build pipeline is automatically triggered when a commit is done onto the main branch.
Build Artifacts Pipeline script :
trigger:
branches:
include:
- main
- release/*
paths:
include:
- synapse-delta/synapse/*
pr: none
variables:
sqlDwPath: 'synapse/synapsepools'
sqlDwSolutionName: 'synapsepools'
sqlDwSolution: '$(sqlDwPath)/$(sqlDwSolutionName).sqlproj'
buildPlatform: 'Any CPU'
buildConfiguration: 'Output'
stages:
- stage: 'publish_artifacts'
displayName: 'Publish Build Artifacts'
jobs:
- job: 'publish_static_artifacts'
displayName: 'Publish Static Artifacts'
pool:
vmImage: 'Ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
inputs:
PathtoPublish: 'synapse'
ArtifactName: 'synapse-artifacts'
displayName: 'Publish Synapse Artifacts'
- job: 'publish_sql_packages'
displayName: 'Publish SQL Packages'
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
steps:
- task: NuGetToolInstaller@1
- task: NuGetCommand@2
inputs:
restoreSolution: '$(sqlDwSolution)'
- task: VSBuild@1
inputs:
solution: '$(sqlDwSolution)'
platform: '$(buildPlatform)'
configuration: 'Release'
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
inputs:
PathtoPublish: '$(sqlDwPath)/bin/$(buildConfiguration)/synapsepools.dacpac'
ArtifactName: 'sql_dw_dacpac'
displayName: 'Publish SQL DACPAC'
Here the Static Artifacts are refering to the python packages / libraries to be installed on the cluster and the SQL Packages step in the build pipleine refers to the dacpac build creation for deployment.
8.Deploy Artifacts onto the main DEV worskpace
Once the artifacts are ready , we have to deploy this to the DEV workspace. We could have it as 1 deployment pipeline , however for this blog we have 2 deployment pipelines one for the sql artifacts (Dedicated SQL Pools) and Python dependencies / packages and the second deployment pipeline for synapse workspace artifacts.
The defintion for the SQL artifacts deployment pipleine .
SQL Deployment Pipeline defenition :
trigger: none
pr: none
resources:
pipelines:
- pipeline: ciartifacts
source: ci-artifacts
trigger:
branches:
- main
stages:
- stage: deploy_to_dev
displayName: 'Deploy to DEV' # In DEV, excludes publishing to Synapse workspace as this is a manual publish step
variables:
- group: mdwops-release-dev
jobs:
- template: jobs/deploy-ded-sql-pool.yml
parameters:
environmentName: 'DEV'
serviceConnection: 'SynapseDepolyment'
This script picks up the artifacts from the build artifact which is created from the previous build pipeline. This contains the dacpac and the sql objects (Stored procedures).
The reference Deploy Pipeline Definiton used for dedicated Pool Deployment :
arameters:
- name: environmentName
type: string
- name: serviceConnection
type: string
jobs:
- deployment: deploy_dedicated_sql_pool
displayName: 'Deploy to synapse dedicated sql pool'
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
variables:
sqlProjName: synapsepools
environment: $
strategy:
runOnce:
deploy:
steps:
# https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/tasks/deploy/sql-azure-dacpac-deployment?view=azure-devops
- task: SqlAzureDacpacDeployment@1
inputs:
azureSubscription: $
AuthenticationType: 'server'
ServerName: $(synapseSqlPoolServer).sql.azuresynapse.net
DatabaseName: $(synapseDedicatedSqlPoolDBName)
SqlUsername: '$(synapseSqlPoolAdminUsername)'
SqlPassword: '$(synapseSqlPoolAdminPassword)'
deployType: 'DacpacTask'
DacpacFile: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/ciartifacts/sql_dw_dacpac/$(sqlProjName).dacpac'
AdditionalArguments: '/Variables:ADLSLocation=abfss://datalake@$(datalakeAccountName).dfs.core.windows.net /Variables:ADLSCredentialKey=$(datalakeKey)'
displayName: 'Deploy DACPAC to synapse dedicated sql pool'
To deloy the workspace artifacts we have a separate pipeline.
Workspace deployment pipeline defintion.
trigger: none
pr: none
resources:
repositories:
- repository: synapse_artifacts
type: git
name: synapsedelta/synapse-delta
ref: workspace_publish
stages:
- stage: deploy_to_dev
displayName: 'Deploy to DEV'
variables:
- group: mdwops-release-dev
jobs:
- template: jobs/deploy-synapse-ws.yml
parameters:
environmentName: 'DEV'
serviceConnection: 'SynapseDepolyment'
This script refers to the workspace template file and the parameter file. This will deploy the linked services ,datasets , sql scripts , data flows.
The reference script used to deploy the synapse workspace is defined here :
parameters:
- name: environmentName
type: string
- name: serviceConnection
type: string
jobs:
- deployment: deploy_synapse_workspace
displayName: 'Deploy Synapse Workspace'
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-2019'
environment: $
strategy:
runOnce:
deploy:
steps:
- checkout: synapse_artifacts
path: 'workspace_publish'
- task: Synapse workspace deployment@1
inputs:
TemplateFile: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/workspace_publish/idwdemows/TemplateForWorkspace.json'
ParametersFile: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/workspace_publish/idwdemows/TemplateParametersForWorkspace.json'
azureSubscription: $
ResourceGroupName: '$(rgName)'
TargetWorkspaceName: '$(synapseWorkspaceName)'
DeleteArtifactsNotInTemplate: false
OverrideArmParameters: '-AzureBlobStorage1_connectionString "<PARAM VALUE>" -MoviesSinkMart_connectionString "<PARAM VALUE>" -idwdemows-WorkspaceDefaultSqlServer_connectionString "<PARAM VALUE>"'
For deployment of synapse , we are using the synapse workspace deployment task extension. The workspace template files are pointed to the workspace_publish branch.
This should deploy the scripts as well as the dacpac build onto the target synapse workspace.
These lists the steps needed to setup your CI/CD using azure synapse , in the next blog post we will cover :
- Serverless Artifacts Deployment
- Incremental Deployment
Common Errors :
Encountered with exception:Error: For Artifact : Failure in deployment: Skipped
This occurs due to a lower build version of the synapse workspace extension , make sure that the version is 1.9.3 or higher since the lower versions do not support the lake databases.
For Azure devops check the extension to make sure that the version attached is 1.9.3+
Error during execution: Error: Failed to fetch the deployment status {“code”:”400”,”message”:”CreateOrUpdateNotebook failed
This occurs if the spark pool name is different from the destination spark pool.
Parameterizing this could help , so inside the notebook folders the bigdatapool name could be adjusted. The second option is to keep the names in sync.
For Artifact: kv_supply_chain: ArtifactDeploymentTask status: 403; status message: Forbidden
Check the permissions , if the service principle used for azure devops has the rights (Synapse Administrator) on the workspace to deploy Workspace artifacts.
Encountered with exception:Error: Environment validation failed
This validation failure occurs when the parameters which need to be passed to the workspace are not passed. Make sure to overide parameters.
Error during execution: Error: Failed to parse package: Error: Could not figure out full dependancy model. Some dependancies may not exist in template
This issue happens if the build artifacts created are not of the right resoruce type which is expected by the deployment task. Check if the build artifacts are generating the right resource types which the deployment taks is expecting. For example , the build artifact could be producing a azure dafa factory pipeline rather than a workspace pipeline , which are closely related but not the same.